DK Science: Radioactivity
The atoms of some chemical elements are unstable. They try to rearrange themselves to make more stable atoms. In the process, they give off radiation particles or tiny bursts of radiation. This process is called radioactivity. Although radioactivity can be harmful to people, it can also be important to us in everyday life. It is used to make nuclear energy and preserve food, and it also plays a vital role in the treatment of cancer.
Some types of radioactivity are harmful, because they damage or destroy the tissues of the human body. If people receive large doses of radioactivity, they can become ill with radiation sickness, which often causes cancer. Radiation sickness can also affect people’s ability to have children.
The three types of radiation are alpha and beta particles, and gamma radiation, named after the Greek letters above. An alpha particle is two protons joined to two neutrons. A beta particle is an electron. Gamma radiation is high-energy electromagnetic radiation.
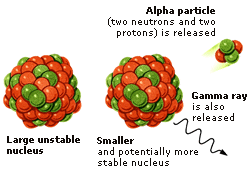
An alpha particle is made when the nucleus (central part) of a large, unstable atom rearranges itself, or decays, to make a smaller, more stable atom. The new and smaller atom has two protons and two neutrons fewer than the original atom. These join together to make the alpha particle that is given off. Some energy is also released as a gamma ray. This is high-energy and high-frequency radiation, travelling at the speed of light.
Beta decay is quite different from alpha decay. One of the neutrons in the nucleus of the unstable atom changes into a proton and an electron. The proton joins onto the nucleus, but the electron is ejected from the atom at high speed. This fast-moving electron is called a beta particle. Some energy is also released as a gamma ray.
Radioactivity can cause cancer if it harms healthy cells in the human body. It can also help to cure cancer if it is used to destroy unhealthy cells. In radiotherapy, a powerful machine fires carefully targeted beams of radiation at tumours (cancer cells) in the patient’s body. The radioactivity destroys the cells and helps to improve the patient’s chances of survival.