Lebanon Map: Regions, Geography, Facts & Figures
Lebanon, officially known as the Lebanese Republic, is a country in Western Asia and is part of the Middle East. It is a primarily Arab nation that is steeped in history, divided into eight governorates, and shares common cultural and linguistic heritage with other countries in the Levant such as Palestine, Jordan, and Syria.
With a population of just over 6 million people, Lebanon is known for its rich cultural heritage and vibrant arts scene. It is a country where East meets West, and where ancient traditions and modern innovations coexist in a dynamic and exciting way.
If you want to discover more in-depth information on Lebanon as a country, check out our Lebanon Profile!
Plus, test your country knowledge with our world geography quiz on Middle Eastern Mythological Creatures.
Lebanon Facts: History
Lebanon has a rich and fascinating history that has been shaped by numerous empires and powers throughout the ages. From the Assyrians to the Babylonians, from the Persian rulers to the Roman emperors, and from the medieval Islamic empire to modern times, Lebanon has a long and complex history that is deeply intertwined with the history of the surrounding region.
The country was under French mandate until 1943, when it gained independence. Lebanon has also faced political instability and conflict, including a civil war that lasted from 1975 to 1990, which has left a lasting impact on the country's political and social landscape, including instability, economic struggles, and environmental issues.
Nevertheless, today, the people of Lebanon remain resilient and determined and are working hard to build a better future for themselves and their country.
Lebanon Facts: Geography
Lebanon is a small yet diverse country that is home to a variety of landscapes, from the Mediterranean coast to the Anti-Lebanon Mountains, and from the Qurnat as Sawda peak (the highest point in Lebanon) to the Beqaa Valley (the country's agricultural heartland).
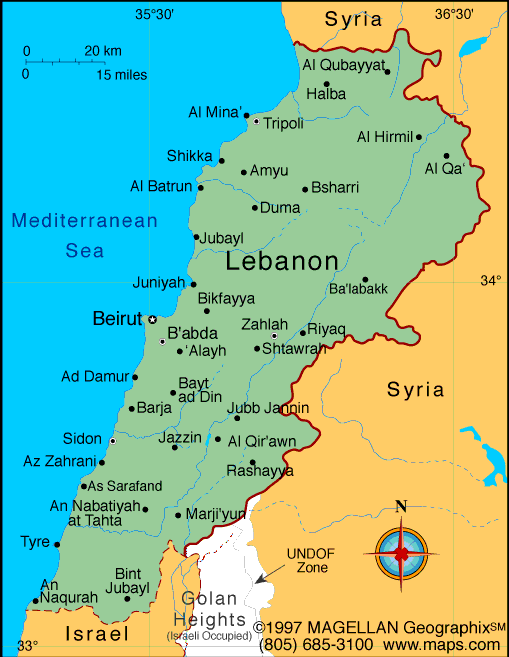
It is bordered by Syrian land to the north and east, Israel to the south, and the Mediterranean Sea to the west. Lebanon is divided into eight governorates, which are further divided into districts and municipalities. The governorates are Beirut, Mount Lebanon, North Lebanon, South Lebanon, Nabatieh, Bekaa, Baalbek-Hermel, and Akkar.
Lebanese Administrative Divisions
Each governorate has its unique cultural and historical significance on the country map of Lebanon. Beirut (or Beyrouth), the capital of Lebanon, is a vibrant cultural and commercial hub, with a rich history and a lively nightlife scene. Mount Lebanon (also known as Mont-Liban) is a mountain range in Lebanon that is known for its natural beauty and historic landmarks. The range is home to the Qadisha Valley, which is a UNESCO World Heritage Site, as well as the Jeita Grotto, which is a series of limestone caves.
North Lebanon is home to the ancient city of Byblos, one of the oldest continuously inhabited cities in the world, with a history dating back to the Neolithic period. South Lebanon is known for its beautiful beaches and coastal cities, such as Tyre and Sidon, which have a rich history dating back to the Phoenician period.
Lebanon Facts: Tourist Attractions
Lebanon is a popular tourist destination known for its rich history, cultural heritage, natural beauty, and major cities. Visitors to Lebanon can explore the country's many historical sites and museums, sample its delicious cuisine, and experience its lively nightlife and music scene, including these attractions:
- Beirut: The stunning and cosmopolitan capital city that is known for its historic landmarks, such as the National Museum of Beirut, the Mohammad Al-Amin Mosque, and the Beirut Souks. The city also has a lively nightlife scene and numerous restaurants serving Lebanese cuisine.
- Byblos: One of the oldest continuously inhabited cities in the world, with a history dating back to the Neolithic period. Byblos is home to ancient ruins, such as the Byblos Castle and the Temple of Baalat Gebal, as well as a picturesque harbor and a vibrant market.
- Sidon: This is a coastal city in Lebanon with a rich history dating back to the Phoenician period. The city is home to historic landmarks, such as the Sidon Sea Castle, the Temple of Eshmun, and the Khan al-Franj market.
- Tripoli: Tripoli is the second-largest city in Lebanon and an important cultural and commercial center. The city is home to historic landmarks, such as the Tripoli Castle, the Al-Mina Archaeological Site, and the Saint Gilles Citadel.
- Mount Lebanon: This mountain range in Lebanon is known for its natural beauty and historic landmarks. The range is home to the Qadisha Valley, which is a UNESCO World Heritage Site, as well as the Jeita Grotto, which is a series of limestone caves.

People Also Ask...
If you're inspecting the Lebanon country map, you may have some queries about the region. Here are some of the most frequently asked questions, along with their answers.
Is Lebanon in Asia or Europe?
According to the world map, Lebanon is located in Western Asia, on the eastern shore of the Mediterranean Sea. Lebanon borders Syria in the north and east, while Israel lies to the south.
What Country Did Lebanon Belong To?
Lebanon was ruled by various powers, including the Assyrians, Babylonians, Persians, and Romans. It was also an important part of the Islamic empire during the medieval period and gained independence from French mandate in 1943 as its own country.
What Is Lebanon Famous For?
Lebanon is famous for its history, culture, and heritage. The country's cuisine, including dishes such as hummus, tabbouleh, and shawarma, is also well-known. Lebanon is a popular tourist destination, with attractions such as Beirut, Byblos, Sidon, Tripoli, the Qadisha Valley, and Jeita Grotto.